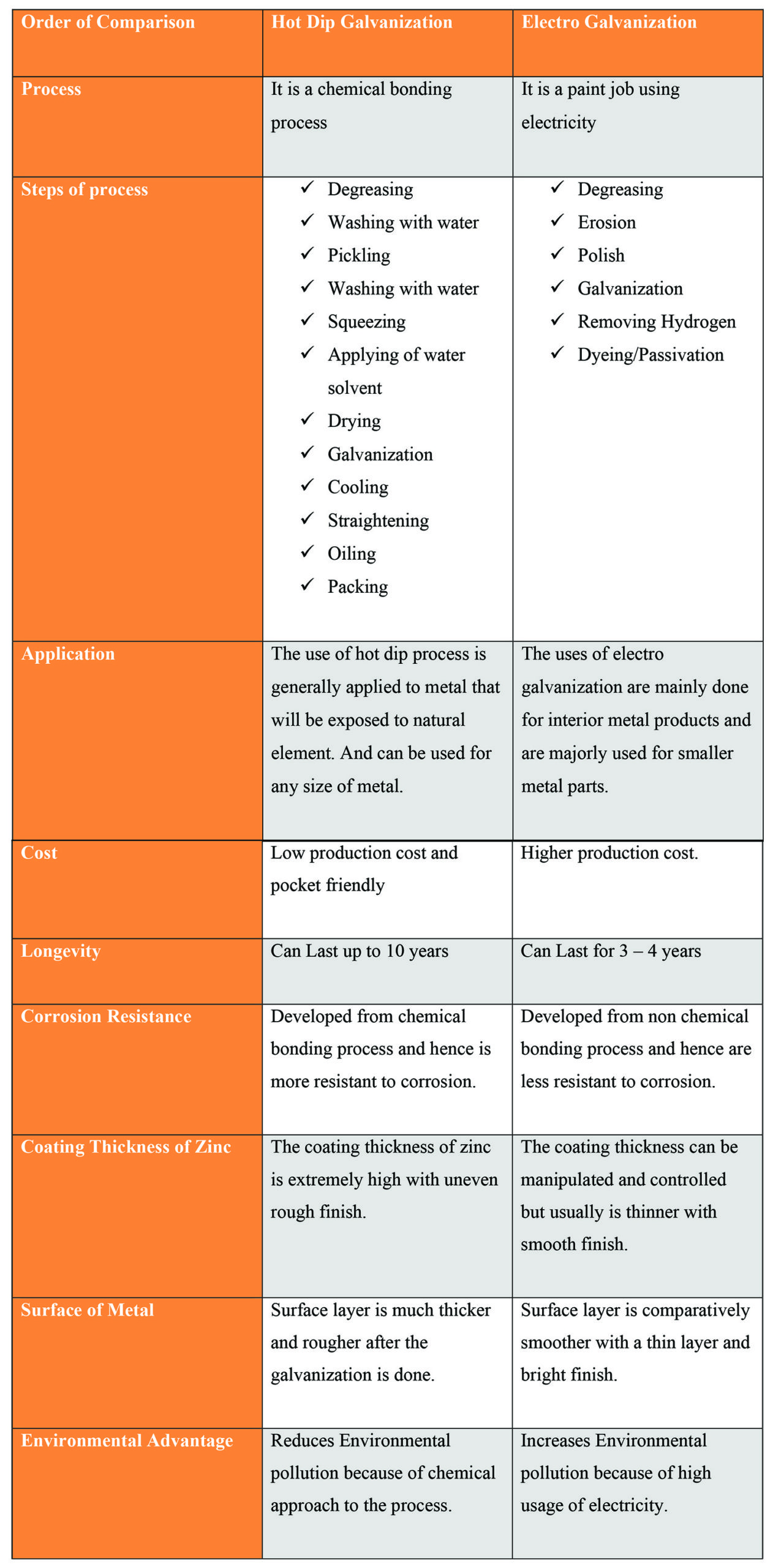
Hot Dip Galvanizing process is a work that comes with numerous types of defects. Today we will be discussing and explaining the causes of defects and variations that arise in its appearance.
The detail listing for these Galvanised Steel Coating are listed below. Let us get to know about them in-depth.
Defects in Galvanized Steel Coatings
Ungalvanized Weld Areas
The coating that is missed on the areas welded, senses the presence of welding slags. These details are monitored on the welds, thus it is core responsibility of a fabricator to ensure that they remove all the welding slags before the galvanizers are dispatched to the respective unit.
Dark Staining Adjacent to Welds
During the galvanizing process it is necessary that the steel coating is not missed. Here it is necessary to prepare the chemicals that help penetrate the unsealed overlaps on the galvanizers. If these galvanizers have poor quality welds, that needs to be boiled at the time of galvanization. The entire process causes the missing coating and the surface is left contaminated at the time of galvanizing.
Furthermore,anhydrous fluxing salts that are available on the connection will absorb the atmospheric moisture and will leach the galvanizing surface. The complete process of leaching of these salts will reach equilibrium. Hence, it is necessary that the areas are washed properly and no left particles are available during the leaching process and its work.
Dull Gray or Mottled Coatings
The production of thicker galvanized coating will be at the duller side as compared to regular coatings. It is due to the use of reactive steel. These coatings possess a longer life and the only reason for it is because it has greater thickness and higher appearance. All this is not in anyone’s control and the functionality of steel metallurgy is different from regular Galvanized Steel Coatings process.
Dross Pimples/Inclusions
The development process of dross occurs when the galvanization is in the form of zinc-iron crystals. Here the melting point will be at the higher side as compared to the metal in the zinc bath. The drosses that are trapped on the coating of galvanizers will be giving a gritty or rough look. The active components of dross additions is the coating is not harming the performance level. Here the corrosion resistance of zinc dross matches the coating that is available at the galvanizing process.
White Storage Staining
The steel galvanizing coating once done will be stored in wet places with items stacked. Here it is something that will not be in a well-ventilated condition which will react with the atmospheric moisture and develop a hefty amount of white zinc hydroxide deposits on the surface of the galvanizing coating.
Ash Staining
It is a responsibility of fabricatore to make sure that the zinc ashes are developed during the galvanizing process that is immersing in the zinc. These are the molten zinc staked at the bottom of the galvanizers while getting it removed from the galvanizing bath. It is observed that these ashes are trapped where it is not possible to reach, hence it gets stuck to the outer side of the coating at the time of work when removal process is done from the bath. These ashes may be available in lighter brown stain or a dull surface appearance after the complete removal process. It does not get impacted with the overall performance of the galvanized steel coating.
Runs, Drainage Spikes, and Puddling
During the hot-dip galvanizing process, there are defects that cannot be avoided for regular items, and these cannot be tolerated for a longer time. It is because it does not affect the assembly and the functionality of the item. Here it also poses a way for safety risk to get handling of the services accurately.
Bare Patches
The patches occur in uncoated areas of the galvanized work. The core reason to it is due to the non preparing of the surface precisely and properly. It will further be considered as an insufficient pretreatment in degreasing, and pre-fluxing. Thus it is necessary that the fabricator works in these respective areas with the help of suggested techniques for the galvanizing process.
Rust Staining
To remove the rust and stain from the galvanized coating it is necessary to use wire brushing. The uncoated steel is exposed from these steel coatings and will quicken corrosion and strain where the contact occurs.
Similarly there are multiple reasons and causes that occur in Galvanised Coatings. But with our manufacturing organization we help our clients meet their expectations and deliver them hassle-free work.
Dark Staining Adjacent to Welds
During the galvanizing process it is necessary that the steel coating is not missed. Here it is necessary to prepare the chemicals that helps penetrate the unsealed overlaps on the galvanizers. If these galvanizers have poor quality welds, that needs to be boiled at the time of galvanization. The entire process causes the missing of coating and the surface is left contaminated at the time of galvanizing.
Furthermore, anhydrous fluxing salts that are available on the connection will absorb the atmospheric moisture and will leach the galvanizing surface. The complete process of leaching of these salts will reach equilibrium. Hence, it is necessary that the areas are washed properly and no left particles are available during the leaching process and its work.
Dull Gray or Mottled Coatings
The production of thicker galvanized coating will be at the duller side as compared to regular coatings. It is due to the use of reactive steel. These coatings possess a longer life and the only reason to it is because it has greater thickness and higher appearance. All this is not in anyone’s control and the functionality of steel metallurgy is different from regular Galvanized Steel Coatings process.
Dross Pimples/Inclusions
The development process of dross occurs when the galvanization is in the form of zinc-iron crystals. Here the melting point will be at the higher side as compared to the metal in the zinc bath. The drosses that are trapped on the coating of galvanizers will be giving a gritty or rough look. The active components of dross additions is the coating is not harming the performance level. Here the corrosion resistance of zinc dross matches the coating that is available at the galvanizing process.
White Storage Staining
The steel galvanizing coating once done will be stored in wet places with items stacked. Here it is something that will not be in a well-ventilated condition which will react with the atmospheric moisture and develop a hefty amount of white zinc hydroxide deposits on the surface of the galvanizing coating.
Ash Staining
It is a responsibility of fabricatore to make sure that the zinc ashes are developed during the galvanizing process that is immersing in the zinc. These are the molten zinc staked at the bottom of the galvanizers while getting it removed from the galvanizing bath. It is observed that these ashes are trapped where it is not possible to reach, hence it gets stuck to the outer side of the coating at the time of work when removal process is done from the bath. These ashes may be available in lighter brown stain or a dull surface appearance after the complete removal process. It does not get impacted with the overall performance of the galvanized steel coating.
Runs, Drainage Spikes, and Puddling
During the hot-dip galvanizing process, there are defects that cannot be avoided for regular items, and these cannot be tolerated for a longer time. It is because it does not affect the assembly and the functionality of the item. Here it also poses a way for safety risk to get handling of the services accurately.
Bare Patches
The patches occurs in uncoated areas of the galvanized work. The core reason to it is due to the non preparing of the surface precisely and properly. It will further be considered as an insufficient pretreatment in degreasing, and pre-fluxing. Thus it is necessary that the fabricator works in these respective areas with the help of suggested techniques for the galvanizing process.
Rust Staining
To remove the rust and stain from the galvanized coating it is necessary to use wire brushing. The uncoated steel is exposed from these steel coatings and will quicken corrosion and strain where the contact occurs.
Similarly there are multiple reasons and caused that occurs in Galvanised Coatings. But with our manufacturing organization we help our clients meet their expectation and deliver them hassle-free work.
Final Words
Galvanizers, is the leading manufacturing unit that helps its clients overcome all such defects and causes which lead to easy accommodation of the work with details and proper deliverables.